Content Security Policy
An attacker may attempt to deliver malicious scripts or inject unwanted data into your site using cross-site scripting (XSS) or data injection attacks. By default, the browser executes resources from any origin without restriction, as it doesn’t know whether a source is trusted. A malicious script can then access cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information stored by the browser. To secure your site against such attacks, the Content Security Policy (CSP) provides a standardized set of directives that instruct the browser on which content sources are allowed and which should be restricted.
How It Works
The Content Security Policy (CSP) utilizes the Content-Security-Policy response header to restrict resource loading from unknown domains, allowing only those resources that come from a configured list of trusted domains for each content type. To prevent the execution of malicious resources-such as styles, scripts, fonts, images, connects, and frames-from unknown domains on your site, configure the CSP with specific directives in Bold Reports®.
Will enabling Content Security Policy (CSP) affect existing report rendering?
Enabling Content Security Policy (CSP) will not affect report rendering unless the resources loaded within the reports are requested from unknown domains, and those URLs are not excluded from the CSP settings. If you intend to load resources for your reports from an external URL, you must include that URL in the appropriate sources section of the CSP settings.
Content Security Policy Configuration
Configure the Content Security Policy in the Security settings under the Settings section within Bold Reports®.
By default, the Content Security Policy is disabled, allowing sources from all domains without restriction. As a result, the Content-Security-Policy response header will not be added to the request.

Enabling Content Security Policy
If you enable the Content-Security-Policy option, the Content-Security-Policy response header will be added to the request, including the default allowed domain values for each source.

Policy Configuration for Style Source
The style-src directive allows only the URLs of style sheets that are added in the Style Source field and restricts style sheets from other URLs.
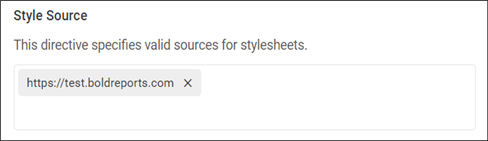
The permitted URLs will be added to the Content-Security-Policy for the style source.
Content-Security-Policy: style-src 'self' https://test.boldreports.com
Policy Configuration for Script Source
The script-src directive allows only JavaScript sources from URLs added in the Script Source field and restricts script sources from other URLs.
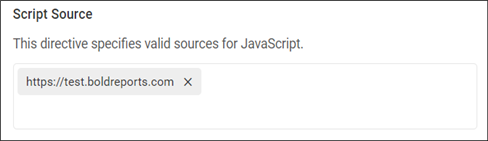
The permitted URLs will be added to the Content-Security-Policy for the script source as follows:
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' https://test.boldreports.com
Policy Configuration for Font Source
The font-src directive allows font sources only from URLs added in the Font Source field and restricts font sources from other URLs.
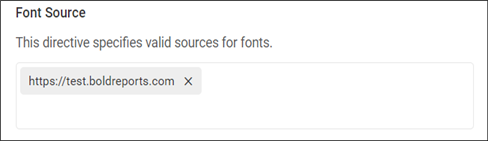
The permitted URLs will be added to the Content-Security-Policy for the font source as follows:
Content-Security-Policy: font-src 'self' https://test.boldreports.com
Policy Configuration for Image Source
The img-src directive allows images only from URLs added in the Image Source field and restricts image sources from other URLs.
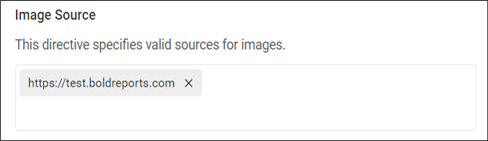
The permitted URLs will be added to the Content-Security-Policy for the image source as follows:
Content-Security-Policy: img-src 'self' https://test.boldreports.com
Policy Configuration for Connect Source
The connect-src directive allows Fetch/XHR requests only from URLs added in the Connect Source field and restricts Fetch/XHR requests from other URLs.
The permitted URLs will be added to the Content-Security-Policy for the connect source as follows:
Content-Security-Policy: connect-src 'self' https://test.boldreports.com
Policy Configuration for Frame Source
The frame-src directive allows sources for nested documents to use elements such as <frame> and <iframe> only from URLs added in the Frame Source field, and restricts sources from other URLs.
The permitted URLs will be added to the Content-Security-Policy for the frame source.
Content-Security-Policy: frame-src 'self' https://test.boldreports.com
- How It Works
- Will enabling Content Security Policy CSP affect existing report rendering
- Content Security Policy Configuration
- Enabling Content Security Policy
- Policy Configuration for Style Source
- Policy Configuration for Script Source
- Policy Configuration for Font Source
- Policy Configuration for Image Source
- Policy Configuration for Connect Source
- Policy Configuration for Frame Source
- How It Works
- Will enabling Content Security Policy CSP affect existing report rendering
- Content Security Policy Configuration
- Enabling Content Security Policy
- Policy Configuration for Style Source
- Policy Configuration for Script Source
- Policy Configuration for Font Source
- Policy Configuration for Image Source
- Policy Configuration for Connect Source
- Policy Configuration for Frame Source