Bold Reports® in the Microsoft Azure Marketplace
This section explains how to use Bold Reports® in the Azure portal to select and create the Bold Reports® Server virtual machine.
Pre-configured image via Azure Marketplace
One of the fastest ways to get Bold Reports® Server up and running in Azure is based on the pre-configured server image through the Azure Marketplace.
-
Sign in to the Azure portal.
-
Click on the
Create a resourceoption in the upper left corner.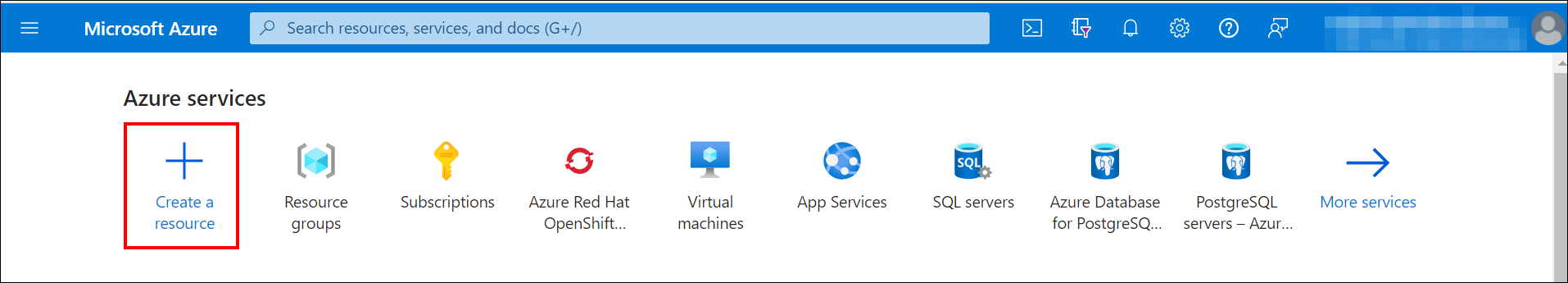
-
Search for
Bold Reports Enterprise.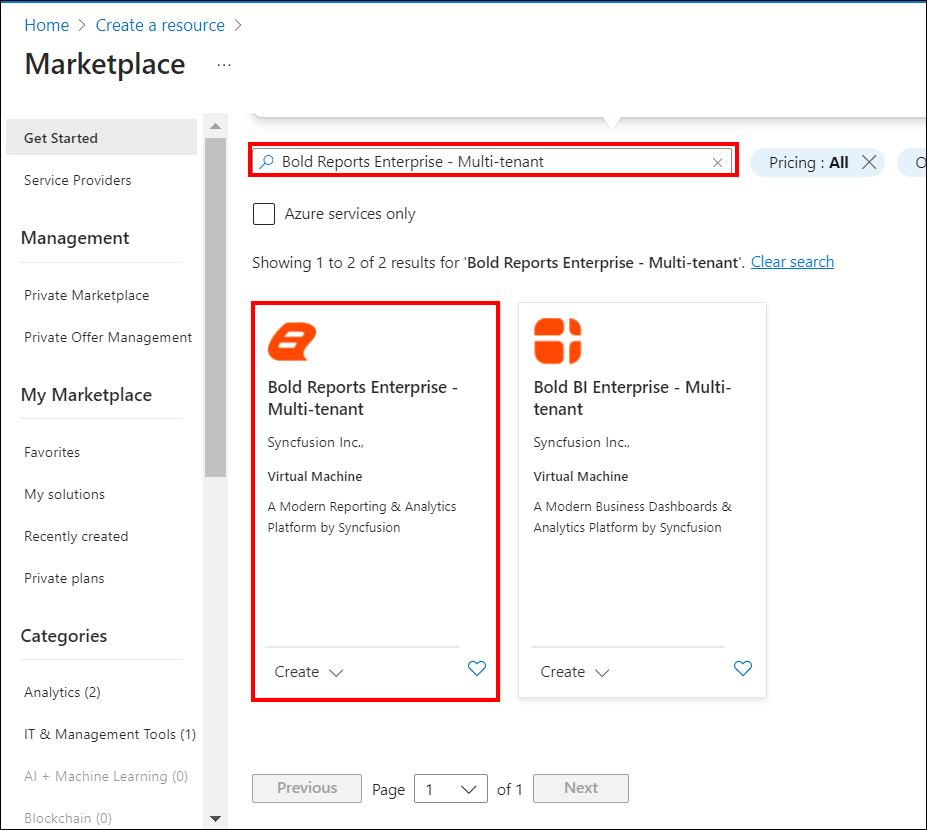
-
Select Bold Reports® Enterprise Multi-tenant and click the
Createbutton.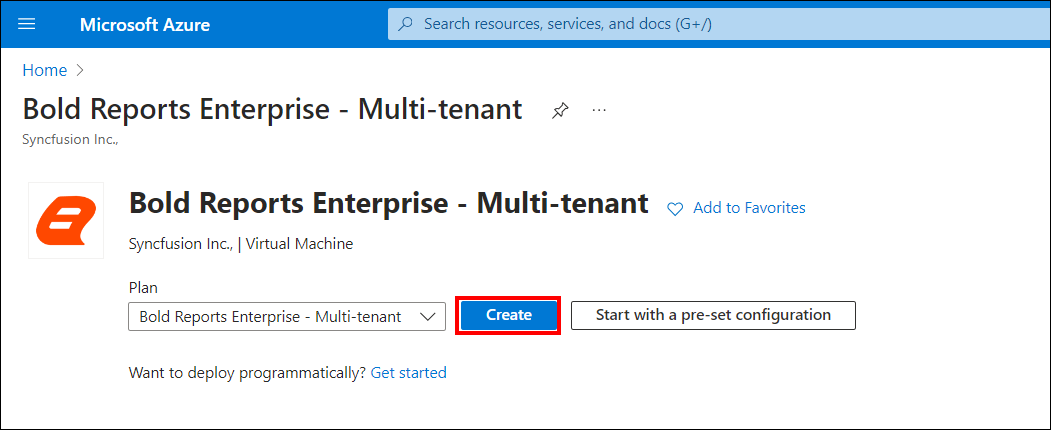
Basics blade
The basics blade requests administrative information for the virtual machine.
*Resource group: Select an existing resource group or type the name for a new one. To learn more about resource groups click here.
*Virtual machine name: Enter a name for the virtual machine. The name must be within 1-15 characters and should not contain special characters.
*Region: Select an Azure data center location where you want to run the VM.
*Size: The default plan is Standard E2 size, but you can change it by selecting the Change Size option.
*Username: Enter a user name to create a local account on the VM. The local account is used to sign in and manage the VM.
*Password: Enter a strong password to create a local account on the VM. The password must be within 12-123 characters and meet three out of the four following complexity requirements: one lowercase character, one uppercase character, one number, and one special character.
-
When finished, click
Nextto proceed to theDisksblade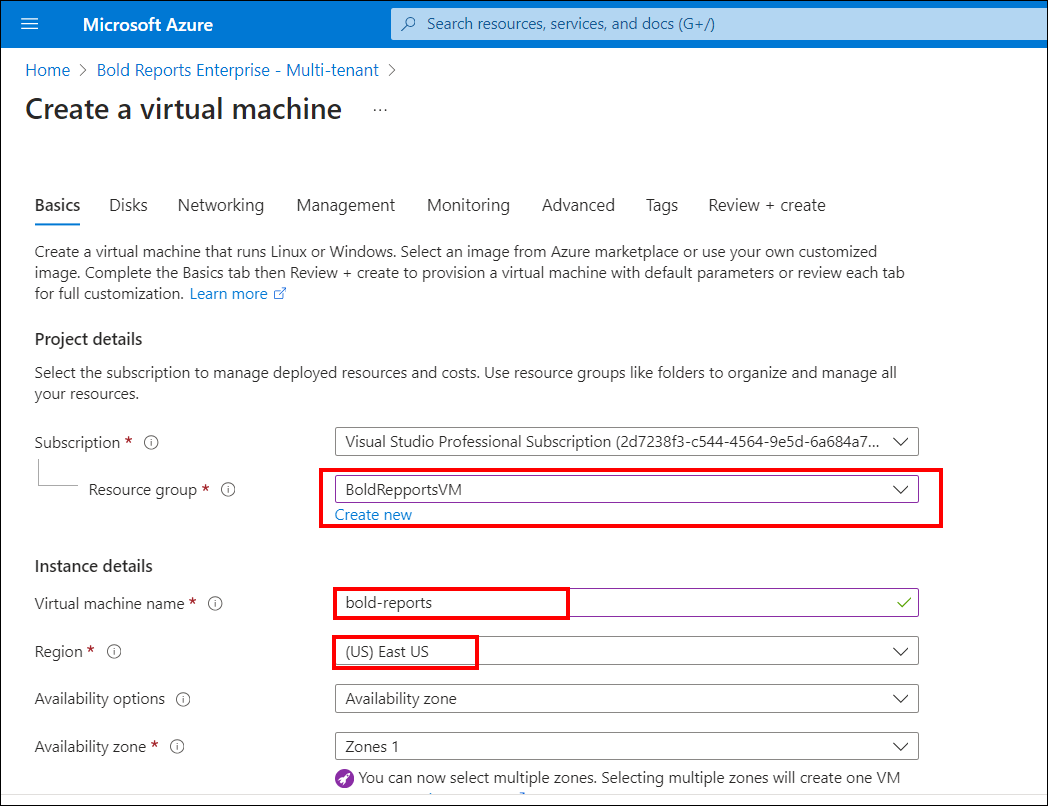
Settings blade
The settings blade requests storage and network options. You can accept the default settings; Azure creates appropriate entries at the required location. If the desired virtual machine size is selected, consider utilizing Azure premium storage by choosing Premium (SSD) as the disk type.
Disks
Storage: Premium disks (SSD), backed by solid-state drives, offer consistent and low-latency performance, providing the best balance between price and performance. They are ideal for I/O-intensive applications and production workloads. On the other hand, standard disks (HDD), backed by magnetic drives, are preferable for applications where data is accessed infrequently. When all the changes are completed, click OK.
Use managed disks: Enable this feature to automatically manage disk availability in Azure, providing data redundancy and fault tolerance without the need to create and manage storage accounts. Please note that managed disks may not be available in all regions. To learn more about managed disks, click on the managed disks overview document.
Storage account: Disks for Azure virtual machines are created in storage accounts. To learn more about storage accounts, click on the storage accounts overview page.
Networking
Virtual network: Virtual networks in Azure are logically isolated from each other. You can configure their IP address ranges, subnets, route tables, gateways, and security settings, similar to traditional networks in a data center. By default, virtual machines in the same virtual network can access each other.
Subnet: A subnet is a range of IP addresses within a virtual network that can be used to isolate virtual machines from each other or from the Internet.
Public IP address: Use the public IP address to communicate with the virtual machine from outside the virtual network.
Management
*Boot diagnostics: Capture serial console output and screenshots of the virtual machine running on the host to help diagnose startup issues.
*Guest OS diagnostics: Obtain metrics for every minute of the virtual machine. You can use them to create alerts and stay informed about the applications.
*Diagnostics storage account: Metrics are written to the storage account, allowing you to analyze them with your own tools.
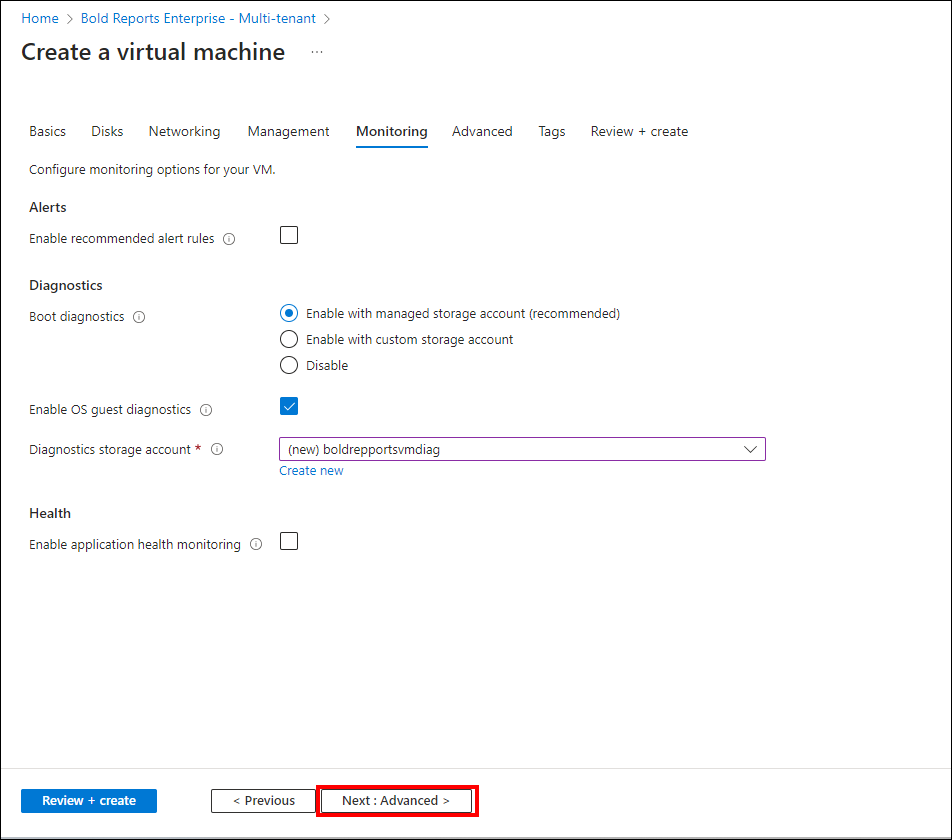
Advanced
*Extensions: Add new features like configuration management or antivirus protection to the virtual machine using extensions. For more information about extensions, visit the extensions documentation
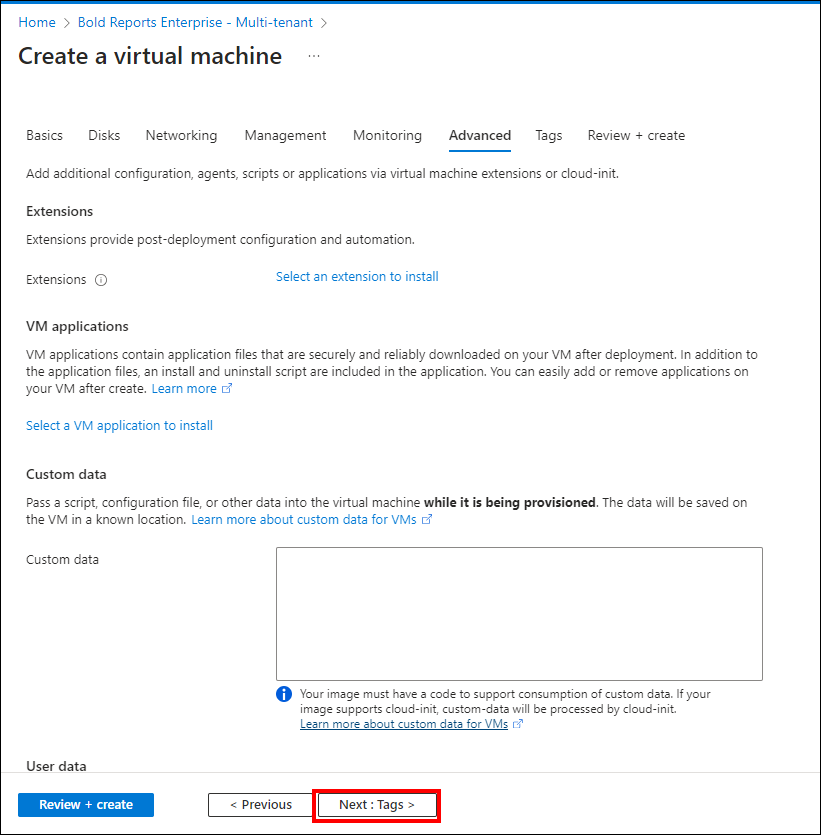
High availability
*Availability set: Group two or more virtual machines in an availability set to provide redundancy to the application. This configuration ensures the availability of at least one virtual machine and meets the 99.95% Azure SLA during planned or unplanned maintenance events. Note that the availability set of the virtual machine cannot be changed after it is created.
When all the changes are completed, click the Review + Create button.
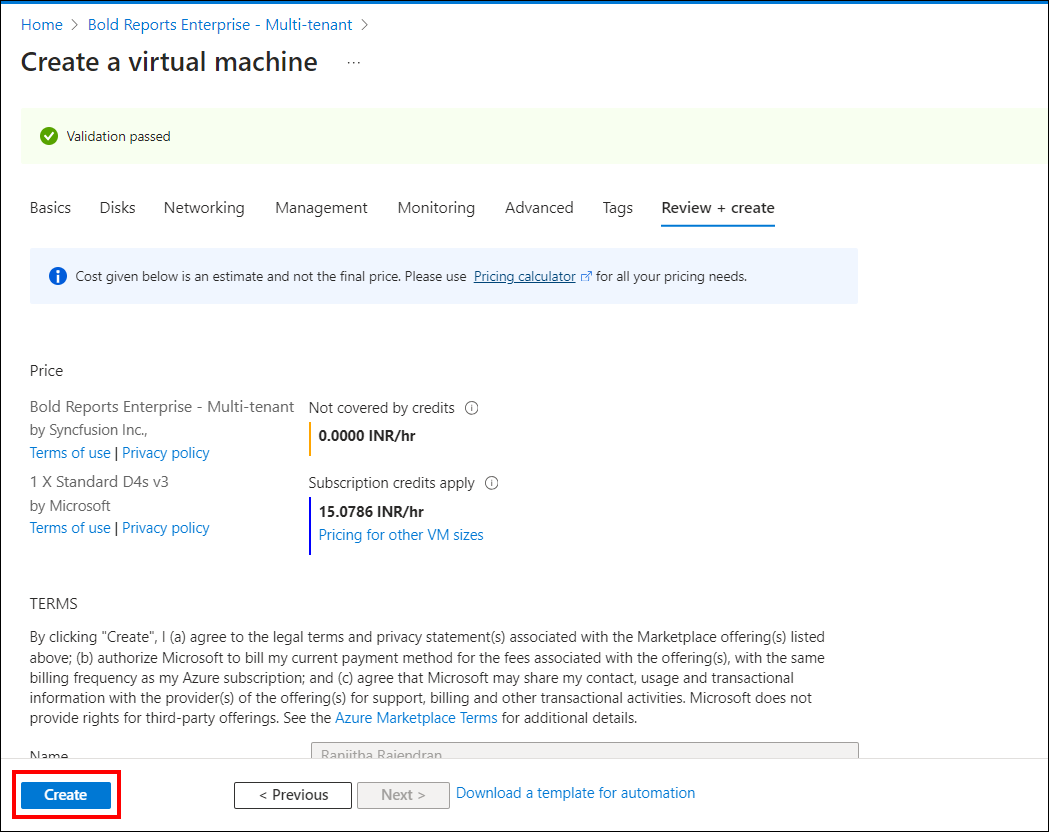
Review and create
-
On the review and create page, click Create to start the Bold Reports® Enterprise - Multi-tenant server virtual machine deployment.
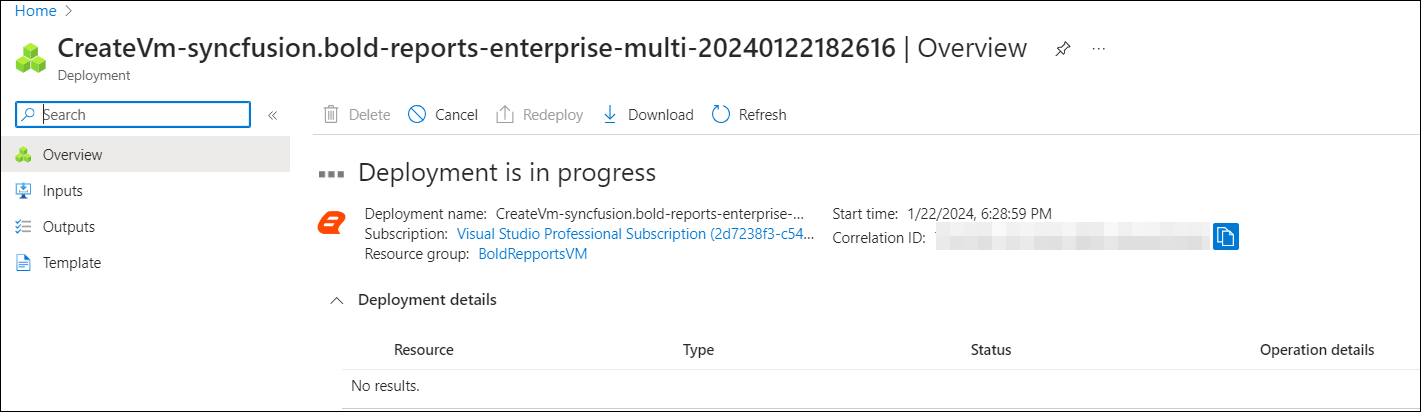
Connect to Bold Reports® Enterprise Multi-tenant Server virtual machine
Once the deployment progress is completed, Bold Reports® Server VM can be connected through a Remote Desktop Connection (RDP). Follow the below steps to connect to the virtual machine:
-
Click
Connecton the virtual machine overview window. A Remote Desktop Protocol (.rdp) file will be downloaded from the Azure portal.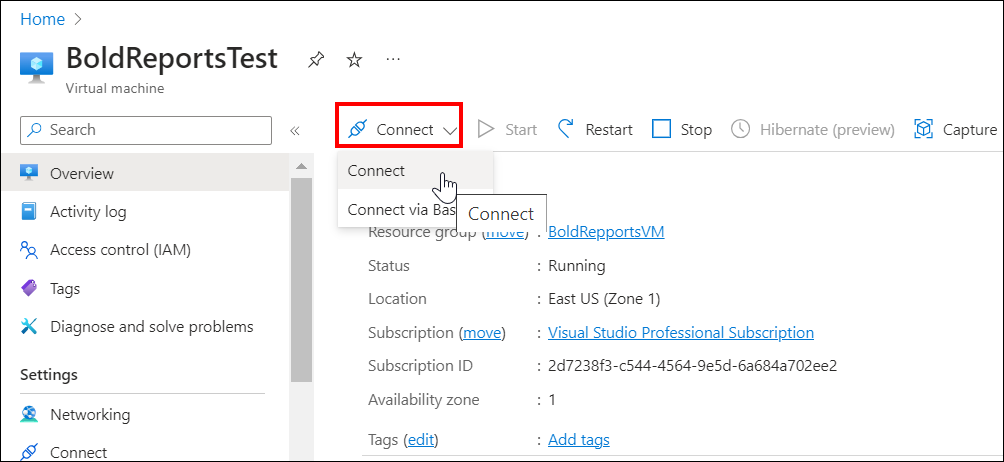
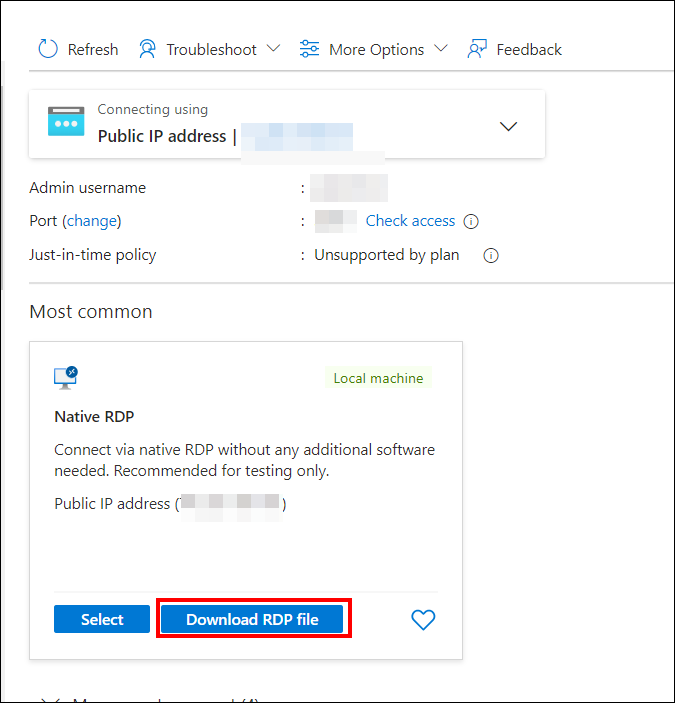
-
Open the .rdp file and click
Connectfor the unknown publisher warning.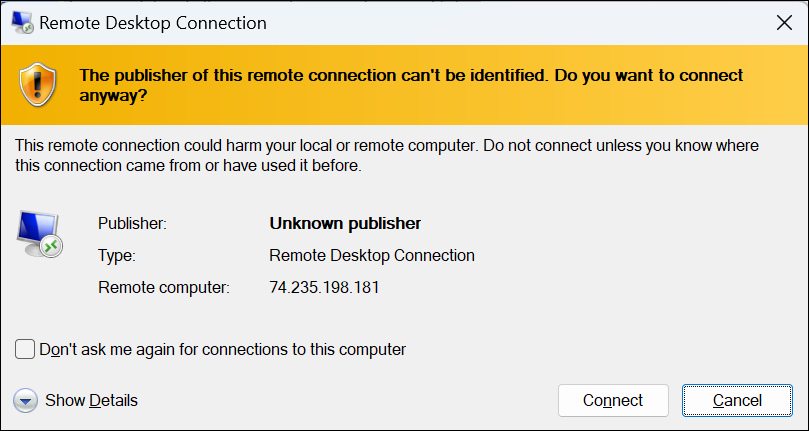
-
Enter the credentials you provided during the VM deployment, as shown below, and click OK.
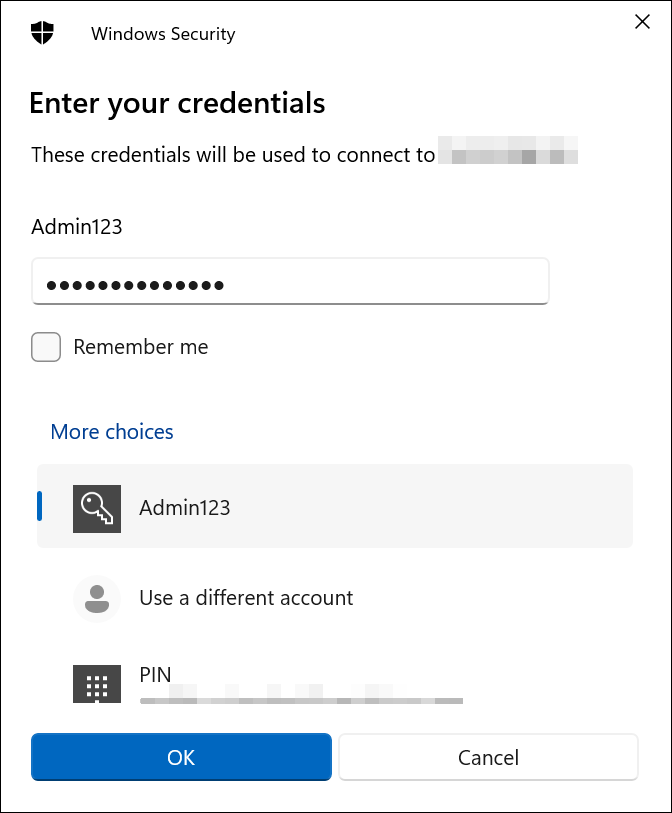
-
On successful connection, the identity verification window will be displayed as shown below. Click
Yesto accept the certificate problems and connect to the virtual machine.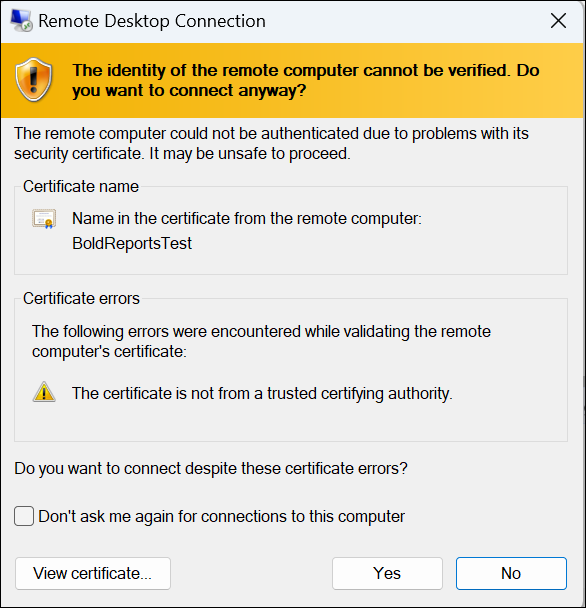
Run the Bold Reports® Server
A desktop shortcut to start the Bold Reports® server can be found once connected to the virtual machine. Follow the steps below to run the Bold Reports® server:
-
Open the
Start Bold Reports<sup>®</sup> in IISshortcut to run the Bold Reports® server. Then, provide the application startup details and complete your setup by selecting the appropriate license.
-
Follow the steps provided in the link to perform the application startup.